- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Bone-Marrow-Derived Mononuclear Cells Relieve Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Nerve Injury in Mice

Read this article at
Abstract
Treating neuropathic pain is a critical clinical issue. Although numerous therapies have been proposed, effective treatments have not been established. Therefore, safe and feasible treatment methods are urgently needed. In this study, we investigated the therapeutic effects of autologous intrathecal administration of bone-marrow-derived mononuclear cells (MNCs) on neuropathic pain. We generated a mouse model of neuropathic pain by transecting the spinal nerve and evaluated neuropathic pain by measuring the mechanical threshold in the following 14 days. Mice in the MNC injection group had a higher mechanical threshold than those in the buffer group. We assessed the effect of MNC treatment on the dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord by immunohistochemistry, mRNA expression, and cytokine assay. The migration and accumulation of microglia were significantly suppressed in the MNC group, and the mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) was markedly downregulated. Furthermore, MNC administration tended to suppress various cytokines in the cerebrospinal fluid of the model mice. In conclusion, our results suggest that intrathecal injection of MNCs relieves neuropathic pain and might be a promising cell therapy for the treatment of this condition.
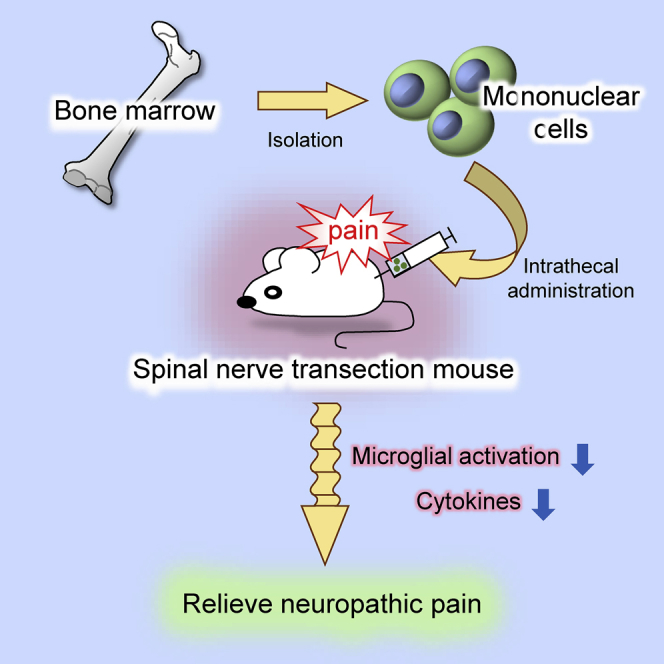
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
Neuropathic pain is an intractable disease. Takamura et al. established a treatment method for neuropathic pain by intrathecal administration of bone marrow derived-mononuclear cells (MNCs) in a spinal nerve transection mouse model. MNC injection relieves neuropathic pain by the suppression of microglial activation and inflammatory cytokine expression.
Related collections
Most cited references42
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Therapeutic angiogenesis for patients with limb ischaemia by autologous transplantation of bone-marrow cells: a pilot study and a randomised controlled trial.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Role of the immune system in chronic pain.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found