- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Polydrug Use among Students in a Public University in a Lower Middle-Income Country
Read this article at
Abstract
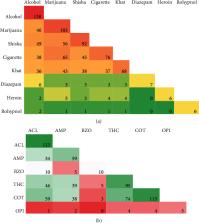
Recreational drug use among students in tertiary institutions remains a public health concern. Despite documentation of drug use in Kenyan universities, most of the studies are based on self-reported history which is prone to social desirability bias. It is in this context that we sought to establish lifetime and current drug use among university students. The study investigated self-reported and confirmed drug use. Using proportionate to size and snowball sampling methods, 380 respondents were enrolled from three university campuses. Actual drug use was confirmed qualitatively using a 6 panel plus alcohol saliva test kit. The study participants' median (IQR) age was 22 (20–23) years, and 262 (69%) were male; 328 (86%) were degree-level students, while 127 (33%) were in their fourth year and above. A total of 221 (58%) students reported a lifetime ever use of drugs, while 193 (51%) tested positive for at least one drug. Alcohol, tobacco products (cotinine), marijuana, and amphetamine or khat were the most preferred drugs. The usage was either solely, concurrently, or simultaneously. Having multiple sexual partners compared to students with no sexual partner (adjusted risk ratio (aRR) of 2.33 (95% CI 1.45, 3.76)) and residing in Mishomoroni and Kisauni (aRR 1.50 (95% CI 1.08, 2.09)) were associated with risk of testing positive for any drug. Having one (aRR of 1.54 (95% CI 1.05, 2.26)) and multiple sexual partners (aRR 2.03 (95% CI 1.27, 3.25) and residing in Mishomoroni and Kisauni (aRR 1.48 (95% CI 1.05, 2.08)) were associated with self-reported drug use. One out of two students was currently using drugs. Irrespective of the method used to record data, alcohol, tobacco products, marijuana, and amphetamine or khat were the most preferred drugs. The usage was solely, concurrently, or simultaneously. Future interventions should focus on continuing students, students' residences, and those who are sexually active.
Related collections
Most cited references71
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Estimating the relative risk in cohort studies and clinical trials of common outcomes.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
The impact of stress on students in secondary school and higher education
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found