- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Unconscious avoidance of eye contact in autism spectrum disorder
Read this article at
Abstract
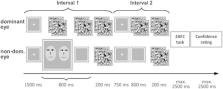
Atypical responses to direct gaze are one of the most characteristic hallmarks of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The cause and mechanism underlying this phenomenon, however, have remained unknown. Here we investigated whether the atypical responses to eye gaze in autism spectrum disorder is dependent on the conscious perception of others’ faces. Face stimuli with direct and averted gaze were rendered invisible by interocular suppression and eye movements were recorded from participants with ASD and an age and sex matched control group. Despite complete unawareness of the stimuli, the two groups differed significantly in their eye movements to the face stimuli. In contrast to the significant positive saccadic index observed in the TD group, indicating an unconscious preference to the face with direct gaze, the ASD group had no such preference towards direct gaze and instead showed a tendency to prefer the face with averted gaze, suggesting an unconscious avoidance of eye contact. These results provide the first evidence that the atypical response to eye contact in ASD is an unconscious and involuntary response. They provide a better understanding of the mechanism of gaze avoidance in autism and might lead to new diagnostic and therapeutic interventions.
Related collections
Most cited references40
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The autism-spectrum quotient (AQ): evidence from Asperger syndrome/high-functioning autism, males and females, scientists and mathematicians.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Bayesian Versus Orthodox Statistics: Which Side Are You On?
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found