- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
RUNX1 Plays an Important Role in Mediating BMP9-Induced Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Line C3H10T1/2, Murine Multi-Lineage Cells Lines C2C12 and MEFs
Read this article at
Abstract
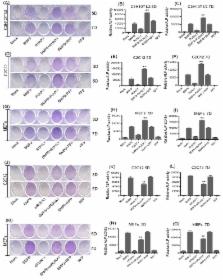
As one of the least studied bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), BMP9 is highly capable of promoting osteogenic differentiation. However, the underlying mechanism involved remains largely unknown. Recent studies have demonstrated that RUNX1 (runt-related transcription factor 1) is essential in osteoblast/chondrocyte maturation. In this study, we investigated the function of RUNX1 in BMP9-induced osteogenic of murine mesenchymal stem cell line (C3H10T1/2) and murine multi-lineage cell lines (C2C12 and MEFs). Our data showed that BMP9 promoted the endogenous expression of RUNX1 in C3H10T1/2, C2C12 and MEFs. Moreover, RUNX1 was probably a direct target of BMP9/Smad signaling. BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation was enhanced by overexpression of RUNX1, whereas inhibited by knockdown RUNX1 in C3H10T1/2, C2C12 and MEFs. Further mechanism studies demonstrated that RUNX1 might affect BMP9-induced phosphorylation of Smad1/5/8, but not the phosphorylation of p38 and ERK1/2.Our results suggest that RUNX1 may be an essential modulator in BMP9- induced osteogenic differentiation of MSCs (Mesenchymal stem cells).
Related collections
Most cited references59
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A simplified system for generating recombinant adenoviruses.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Bone morphogenetic proteins: multifunctional regulators of vertebrate development.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found