- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Airway management: induced tension pneumoperitoneum
Abstract
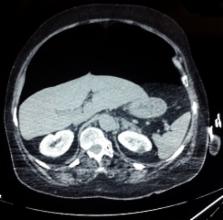
Pneumoperitoneum is not always associated with hollow viscus perforation. Such condition is called non-surgical or spontaneous pneumoperitoneum. Intrathoracic causes remain the most frequently reported mechanism inducing this potentially life threatening complication. This clinical condition is associated with therapeutic dilemma. We report a case of a massive isolated pneumoperitoneum causing acute abdominal hypertension syndrome, in a 75 year female, which occurred after difficult airway management and mechanical ventilation. Emergent laparotomy yielded to full recovery. The recognition of such cases for whom surgical management can be avoided is primordial to avoid unnecessary laparotomy and its associated morbidity particularly in the critically ill.
Most cited references8
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A clinical sign to predict difficult tracheal intubation: a prospective study.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found