- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Early Prediction of Refractory Epilepsy in Children Under Artificial Intelligence Neural Network
Read this article at
Abstract
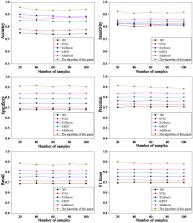
In order to realize the early prediction of refractory epilepsy in children, data preprocessing technology was used to improve the data quality, and the detection model of refractory epilepsy in children based on convolutional neural network (CNN) was established. Then, the data in the epilepsy electroencephalography (EEG) signal public data set was used for model training and the diagnosis of refractory epilepsy in children. Moreover, back propagation neural network (BPNN), support vector machine (SVM), XGBoost, gradient boosting decision tree (GBDT), AdaBoost algorithm were introduced for comparison. The results showed that the early prediction accuracy of BP, SVM, XGBoost, GBDT, AdaBoost, and the algorithm in this study for refractory epilepsy in children were 0.745, 0.778, 0.885, 0.846, 0.874, and 0.941, respectively. The sensitivities were 0.81, 0.826, 0.822, 0.84, 0.859, and 0.918, respectively. The specificities were 0.683, 0.696, 0.743, 0.792, 0.84, and 0.905, respectively. The accuracy was 0.707, 0.732, 0.765, 0.802, 0.839, and 0.881, respectively. The recall rates were 0.69, 0.716, 0.753, 0.784, 0.813, and 0.877, respectively. F1 scores were 0.698, 0.724, 0.759, 0.793, 0.826, and 0.879, respectively. Through the comparisons of the above six indicators, the algorithm proposed in this study was significantly higher than other algorithms, suggesting that the proposed algorithm was more accurate in early prediction of refractory epilepsy in children. Analysis of the EEG characteristics and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images of refractory epilepsy in children suggested that the MRI images of patients' brains under this algorithm had obvious characteristics. The reason for the prediction error of the algorithm was that the duration of epilepsy was too short or the EEG of the patient didn't change notably during the epileptic seizure. In summary, the prediction method of refractory epilepsy in children based on CNN was accurate, which had broad adoption prospects in assisting clinicians in the examination and diagnosis of refractory epilepsy in children.
Related collections
Most cited references21
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
New-onset refractory status epilepticus (NORSE) and febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome (FIRES): State of the art and perspectives
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
