- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Inter-generational nuclear crosstalk links the control of gene expression to programmed genome rearrangement during the Paramecium sexual cycle

Read this article at
Abstract
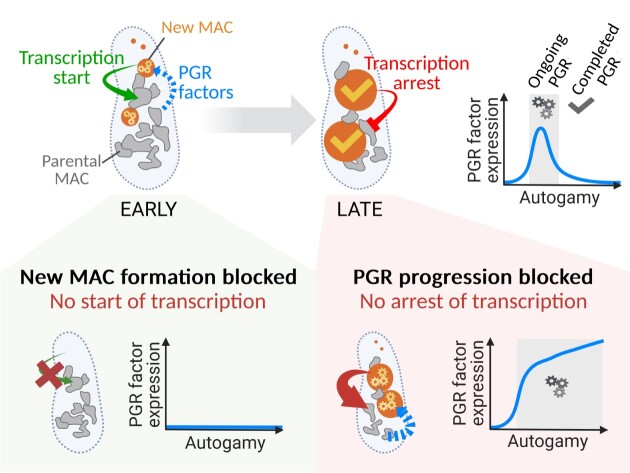
Multinucleate cells are found in many eukaryotes, but how multiple nuclei coordinate their functions is still poorly understood. In the cytoplasm of the ciliate Paramecium tetraurelia, two micronuclei (MIC) serving sexual reproduction coexist with a somatic macronucleus (MAC) dedicated to gene expression. During sexual processes, the MAC is progressively destroyed while still ensuring transcription, and new MACs develop from copies of the zygotic MIC. Several gene clusters are successively induced and switched off before vegetative growth resumes. Concomitantly, programmed genome rearrangement (PGR) removes transposons and their relics from the new MACs. Development of the new MACs is controlled by the old MAC, since the latter expresses genes involved in PGR, including the PGM gene encoding the essential PiggyMac endonuclease that cleaves the ends of eliminated sequences. Using RNA deep sequencing and transcriptome analysis, we show that impairing PGR upregulates key known PGR genes, together with ∼600 other genes possibly also involved in PGR. Among these genes, 42% are no longer induced when no new MACs are formed, including 180 genes that are co-expressed with PGM under all tested conditions. We propose that bi-directional crosstalk between the two coexisting generations of MACs links gene expression to the progression of MAC development.
Graphical Abstract
Related collections
Most cited references75

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
FIMO: scanning for occurrences of a given motif

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found