- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Continuous Monitoring of Vital Signs Using Wearable Devices on the General Ward: Pilot Study
Abstract
Background
Measurement of vital signs in hospitalized patients is necessary to assess the clinical situation of the patient. Early warning scores (EWS), such as the modified early warning score (MEWS), are generally calculated 3 times a day, but these may not capture early deterioration. A delay in diagnosing deterioration is associated with increased mortality. Continuous monitoring with wearable devices might detect clinical deterioration at an earlier stage, which allows clinicians to take corrective actions.
Objective
In this pilot study, the feasibility of continuous monitoring using the ViSi Mobile (VM; Sotera Wireless) and HealthPatch (HP; Vital Connect) was tested, and the experiences of patients and nurses were collected.
Methods
In this feasibility study, 20 patients at the internal medicine and surgical ward were monitored with VM and HP simultaneously for 2 to 3 days. Technical problems were analyzed. Vital sign measurements by nurses were taken as reference and compared with vital signs measured by both devices. Patient and nurse experiences were obtained by semistructured interviews.
Results
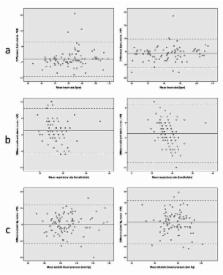
In total, 86 out of 120 MEWS measurements were used for the analysis. Vital sign measurements by VM and HP were generally consistent with nurse measurements. In 15% (N=13) and 27% (N=23) of the VM and HP cases respectively, clinically relevant differences in MEWS were found based on inconsistent respiratory rate registrations. Connection failure was recognized as a predominant VM artifact (70%). Over 50% of all HP artifacts had an unknown cause, were self-limiting, and never took longer than 1 hour. The majority of patients, relatives, and nurses were positive about VM and HP.
Related collections
Most cited references46
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Wireless pulmonary artery haemodynamic monitoring in chronic heart failure: a randomised controlled trial.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found