- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Long noncoding RNA lncTCF7, induced by IL-6/STAT3 transactivation, promotes hepatocellular carcinoma aggressiveness through epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Accumulating evidence suggests the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) in tumor microenvironment may promote the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the underlying mechanism remains largely unknown.
Methods
The expression and promoter activity of lncTCF7 were measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and luciferase reporter assay. The function of the STAT3 binding site in the lncTCF7 promoter region was tested by luciferase reporter assay with nucleotide substitutions. The binding of STAT3 to the lncTCF7 promoter was confirmed by chromatin immunoprecipitation assay (CHIP) in vivo. The effects of decreasing STAT3 with small interference RNA and inhibiting STAT3 activation by small molecular inhibitor on lncTCF7 expression were also determined.
Results
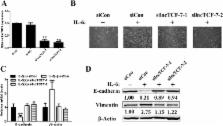
We demonstrate that IL-6 could induce lncTCF7 expression in a time- and dose-dependent manner, and we showed that IL-6 transcriptionally activated the expression of lncTCF7 in HCC cells by activating STAT3, a transcription activator which binds to promoter regions of lncTCF7. Furthermore, knocking-down STAT3 and inhibiting STAT3 activation reduced lncTCF7 expression. Importantly, RNA interference-based attenuation of lncTCF7 prevented IL-6-induced EMT and cell invasion.
Related collections
Most cited references20
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway is required for growth of CD44⁺CD24⁻ stem cell-like breast cancer cells in human tumors.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States: where are we? Where do we go?
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found