- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Comparative study of the Ambu® AuraOnce™ laryngeal mask and endotracheal intubation in anesthesia airway management during neurosurgery
Read this article at
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the feasibility and efficacy of the Ambu® AuraOnce™ laryngeal mask (LMA) compared with endotracheal intubation (ETI) during supratentorial tumor resection in the right lateral decubitus position.
Methods
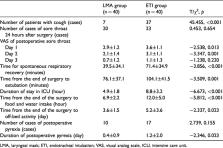
This was a randomized controlled trial of LMA compared with ETI in patients who were scheduled to undergo supratentorial tumor resection in the right lateral decubitus position. The patients were randomized to the LMA (n = 40) and ETI groups (n = 40). The hemodynamic parameters (primary outcome) and mechanical ventilation parameters, anesthetic dose, and complications as well as quality of anesthesia recovery (secondary outcomes) were compared.
Results
Patients in the LMA group exhibited lower mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR) compared with ETI. Nine and two patients received esmolol during intubation and extubation, respectively. The airway pressure (AP) in the LMA group was higher compared with the ETI group 60 minutes after the start of surgery. Compared with the ETI group, the sufentanil dose was lower by 24% and the anesthesia recovery rate was better in the LMA group.
Related collections
Most cited references39
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Pharmacokinetic model driven infusion of propofol in children.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Comparison of four methods for assessing airway sealing pressure with the laryngeal mask airway in adult patients.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found