- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Identification of key pharmacodynamic markers of American ginseng against heart failure based on metabolomics and zebrafish model
Read this article at
Abstract
Background: American ginseng ( Panax quinquefolium L., AG) is a traditional Chinese medicine with multiple cardiovascular protective properties. Many bioactive components have been discovered in AG over these years. However, the understanding of these key pharmacodynamic components of activity against heart failure is insufficient.
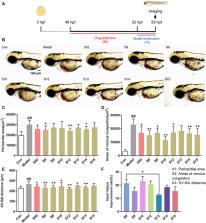
Methods: A heart failure model was established using AB line wild-type zebrafish ( Danio rerio) to evaluate the anti-heart failure activity of AG. Untargeted metabolomics analysis based on ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole electrostatic field orbitrap-mass spectrometry technology (UHPLC-QE-Orbitrap-MS) was performed to screen differential components from AG samples. The potential active components were verified using the zebrafish model. Simultaneously, network pharmacology and molecular docking techniques were used to predict the possible mechanism. Finally, the key targets of six key pharmacodynamic components were verified in zebrafish using quantitative real-time-polymerase chain reaction (Q-PCR) techniques.
Results: The heart failure model was successfully established in 48 h of post-fertilization (hpf) zebrafish larvae by treating with verapamil hydrochloride. The zebrafish assay showed that the anti-heart failure effects of AG varied with producing regions. The result of the herbal metabolomic analysis based on UHPLC-QE-Orbitrap-MS indicated that ginsenoside Rg3, ginsenoside Rg5, ginsenoside Rg6, malic acid, quinic acid, L-argininosuccinic acid, 3-methyl-3-butenyl-apinosyl (1→6) glucoside, pseudoginsenoside F11, and annonaine were differential components, which might be responsible for variation in efficacy. Further analysis using zebrafish models, network pharmacology, and Q-PCR techniques showed that ginsenoside Rg3, ginsenoside Rg5, ginsenoside Rg6, malic acid, quinic acid, and pseudoginsenoside F11 were the pharmacodynamic markers (P-markers) responsible for anti-heart failure.
Conclusion: We have rapidly identified the P-markers against heart failure in AG using the zebrafish model and metabolomics technology. These P-markers may provide new reference standards for quality control and new drug development of AG.
Related collections
Most cited references49

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Network Pharmacology Databases for Traditional Chinese Medicine: Review and Assessment
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Identification of bioactive metabolites using activity metabolomics
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found