- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Assessment of Mastectomy Skin Flaps for Immediate Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction
Read this article at
Abstract
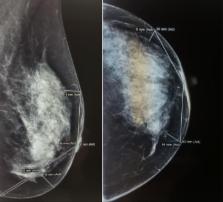
Objectives: The aim of this study is to identify the appropriate preoperative evaluation methods for the quality of the skin flaps and subcutaneous breast layer using different imaging techniques in correlation with the intraoperative findings and also their importance for the outcome in immediate implant-based breast reconstruction.
Materials and Methods: Clinical evaluation, mammography, breast ultrasound and breast MRI were used for the assessment of the mastectomy skin flaps which enhanced the selection of the adequate surgical technique for breast reconstruction. The evaluation started with the skin flap measurement of 50 patients with breast cancer, who were candidates for modified radical mastectomy (MRM) in 2014, using the above-mentioned methods, without immediate breast reconstruction. Consequently, 46 nipple-sparing mastectomies (NSM) and 21 skin-sparing mastectomies (SSM) with immediate breast reconstruction with implants were performed between 2014 and 2017 after having such a preoperative subcutaneous tissue thickness evaluation.
Results: The intraoperative findings of the MRM group showed a 90% accuracy for the MRI preoperative evaluation, 87% for the ultrasound, 81% for the mammography and 71% for the pinch test. The preoperative measurements for the patients undergoing SSM or NSM were a criterion for choosing the surgical technique for breast reconstruction. The rate of postoperative complications was low.
Conclusion: Preoperative clinical measurements, breast ultrasound, breast MRI and mammography can enhance the prediction of the skin flap thickness and thus lead to a low rate of complications and good aesthetic results in implant-based immediate breast reconstruction.
Related collections
Most cited references21
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The ability of intra-operative perfusion mapping with laser-assisted indocyanine green angiography to predict mastectomy flap necrosis in breast reconstruction: a prospective trial.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Nipple sparing mastectomy: can we predict the factors predisposing to necrosis?
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found