- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Aversive Event Anticipation Affects Connectivity between the Ventral Striatum and the Orbitofrontal Cortex in an fMRI Avoidance Task
Read this article at
Abstract
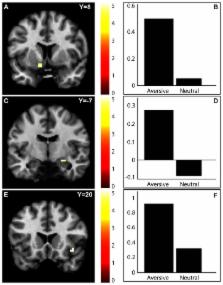
Ability to anticipate aversive events is important for avoiding dangerous or unpleasant situations. The motivation to avoid an event is influenced by the incentive salience of an event-predicting cue. In an avoidance fMRI task we used tone intensities to manipulate salience in order to study the involvement of the orbitofrontal cortex in processing of incentive salience. In the task, cues predicting either aversive or neutral avoidable tones were presented. Ventral striatum, amygdala and anterior insula activations were significantly stronger during presentation of cues for aversive than neutral tones. A psychophysiological interaction analysis showed stronger connectivity between the ventral striatum and the orbitofrontal cortex during aversive than neutral conditions. The present study shows an interaction between the ventral striatum, a structure previously linked to negative incentive salience, and the orbitofrontal cortex supporting a role for this region in processing salience. In addition, this study replicates previous findings suggesting that the task is robust.
Related collections
Most cited references30
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The role of the medial frontal cortex in cognitive control.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Getting formal with dopamine and reward.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found