- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The energetic cost of allostasis and allostatic load
Read this article at
Abstract
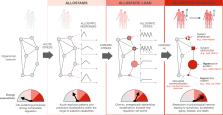
Chronic psychosocial stress increases disease risk and mortality, but the underlying mechanisms remain largely unclear. Here we outline an energy-based model for the transduction of chronic stress into disease over time. The energetic model of allostatic load (EMAL) emphasizes the energetic cost of allostasis and allostatic load, where the “load” is the additional energetic burden required to support allostasis and stress-induced energy needs. Living organisms have a limited capacity to consume energy. Overconsumption of energy by allostatic brain-body processes leads to hypermetabolism, defined as excess energy expenditure above the organism’s optimum. In turn, hypermetabolism accelerates physiological decline in cells, laboratory animals, and humans, and may drive biological aging. Therefore, we propose that the transition from adaptive allostasis to maladaptive allostatic states, allostatic load, and allostatic overload arises when the added energetic cost of stress competes with longevity-promoting growth, maintenance, and repair. Mechanistically, the energetic restriction of growth, maintenance and repair processes leads to the progressive wear-and-tear of molecular and organ systems. The proposed model makes testable predictions around the physiological, cellular, and sub-cellular energetic mechanisms that transduce chronic stress into disease risk and mortality. We also highlight new avenues to quantify allostatic load and its link to health across the lifespan, via the integration of systemic and cellular energy expenditure measurements together with classic allostatic load biomarkers.
Related collections
Most cited references162
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Hallmarks of Aging
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid β.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found