- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Identification of Recurrent Variants in BRCA1 and BRCA2 across Multiple Cancers in the Chinese Population
Read this article at
Abstract
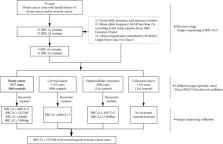
BRCA1 and BRCA2 as important DNA repair genes have been thoroughly investigated in abundant studies. The potential relationships of BRCA1/2 pathogenic variants between multicancers have been verified in Caucasians but few in Chinese. In this study, we performed a two-stage study to screen BRCA1/2 pathogenic variants or variants of uncertain significance (VUS) with 7580 cancer cases and 4874 cancer-free controls, consisting of a discovery stage with 70 familial breast cancer cases and a subsequent validation stage with 7510 cases (3217 breast cancer, 1133 cervical cancer, 2044 hepatocellular carcinoma, and 1116 colorectal cancer). 48 variants were obtained from 70 familial breast cancer cases after BRCA1/2 exon detection, and finally, 20 pathogenic variants or VUS were selected for subsequent validation. Four recurrent variants in sporadic cases ( BRCA1 c.4801A>T, BRCA1 c.3257del, BRCA1 c.440del, and BRCA2 c.7409dup) were identified and three of them were labeled Class 5 by ENIGMA. Two variants ( BRCA1 c.3257del and c.440del) were specific in breast cancer cases, while BRCA2 c.7409dup and c.4307T>C were detected in two hepatocellular carcinoma patients and the BRCA1 c.4801A>T variant in one cervical cancer patient, respectively. Moreover, BRCA1 c.3257del was the most frequent variant observed in Chinese sporadic breast cancer and showed increased proliferation of BRCA1 c.3257del-overexpressing triple-negative breast cancer cell lines (MDA-MB-231) in vitro. In addition to the known founder deleterious mutations, our findings highlight that the recurrently pathogenic variants in breast cancer cases could be taken as candidate genetic screening loci for a more efficient genetic screening of the Chinese population.
Related collections
Most cited references27
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Pathogenic Germline Variants in 10,389 Adult Cancers
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found