- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Effect of endoscopy screening on stage at gastric cancer diagnosis: results of the National Cancer Screening Programme in Korea
Read this article at
Abstract
Background:
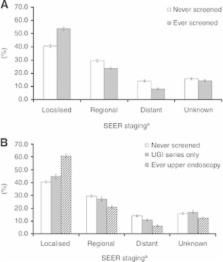
Although gastric cancer screening is common among countries with a high prevalence of gastric cancer, there is little data to support the effectiveness of this screening. This study was designed to determine the differences in stage at diagnosis of gastric cancer according to the screening history and screening method (upper gastrointestinal series (UGIS) vs endoscopy).
Methods:
The study population was derived from the National Cancer Screening Programme (NCSP), a nationwide organised screening programme in Korea. The study cohort consisted of 19 168 gastric cancer patients who had been diagnosed in 2007 and who were invited to undergo gastric cancer screening via the NCSP between 2002 and 2007.
Related collections
Most cited references13
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Gastric cancer treated in 2002 in Japan: 2009 annual report of the JGCA nationwide registry

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Cancer Statistics in Korea: Incidence, Mortality, Survival, and Prevalence in 2011
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found