- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Socio-economic Inequality in Comprehensive Knowledge about HIV in Malawi
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Having comprehensive knowledge about HIV is crucial in the fight against HIV and AIDS, and in achieving the global aspiration of ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030. Low comprehensive knowledge about HIV can undercut efforts to halt the spread of the epidemic. It is important, however, to also determine if socioeconomic inequality is a factor in having a comprehensive knowledge about HIV in order to ensure that socioeconomic considerations are embedded in interventions. In this paper, the objective is to assess trends, as well as socioeconomic related inequality in comprehensive knowledge about HIV in Malawi.
Methods
The current study uses a non-parametric approach and the concentration index. It draws upon secondary data from three rounds of the Malawi Demographic and Health Survey (MDHS) of 2004, 2010 and 2016.
Results
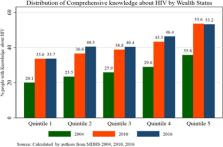
Our results point to an increase in comprehensive knowledge about HIV over the 12-year period, from 28% in 2004 to around 44% in 2016. However, upon using the Erreygers concentration index, a wealth related inequality in comprehensive knowledge about HIV is uncovered. The poorer are less informed and the richer are better informed: comprehensive knowledge about HIV is concentrated among the rich. Furthermore, inequality in comprehensive knowledge about HIV has worsened over this period. Across gender, there is greater inequality among men than women. However, the rural-urban difference in wealth-related inequality in comprehensive knowledge about HIV dropped in 2016.
Conclusion
The results show that comprehensive knowledge about HIV has increased. Furthermore, it is established that comprehensive knowledge about HIV is concentrated among the wealthier in the 2004 -2016 period. Our results suggest that there should be a targeted approach in messaging and disseminating information regarding HIV and AIDS, using methods that are pro-poor.
Related collections
Most cited references26
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Estimating wealth effects without expenditure data--or tears: an application to educational enrollments in states of India.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The bounds of the concentration index when the variable of interest is binary, with an application to immunization inequality.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found