- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Clinical characteristics analysis of 1180 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma secondary to hepatitis B, hepatitis C and alcoholic liver disease
Read this article at
Abstract
Objective
To determine the clinical and liver stiffness characteristics of a cohort of Chinese patients with Hepatocellular carcinoma in different stages of Barcelona clinic liver cancer.
Methods
Details of 1180 patients with Hepatocellular carcinoma referred from October 2014 to November 2017 were collected retrospectively. Demographic data, etiology, clinical, and biochemical details were retrospectively analyzed. The changes of liver stiffness in different etiologies and different stages of Barcelona clinic liver cancer were especially analyzed.
Results
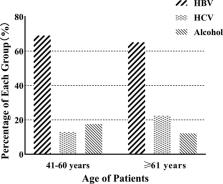
The onset age was 60.33 ± 9.11 (range 24‐84) years, 9 cases were ≤40 years, 572 cases were 41‐60 years, males accounted for 83.92%, females accounted for 16.08%; 599 cases were ≥61 years, males accounted for 78.25%, females accounted for 21.75%. Compared with males, the proportion of females ≥61 is higher than that of men. Majority (n = 787; 66.69%) had HBV infection; second commonest cause was HCV infection (n = 217; 18.39%). More patients with HBV infection were 41‐60 years (69.06%) and were younger than HCV patients. There was no statistical difference in etiology, age, gender, and distribution of diabetes mellitus among different Barcelona clinic liver cancer stages ( P > .05). The overall Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was found to be positively correlated with alkaline phosphatase, γ‐glutamyltransferase, and alpha‐fetoprotein and liver stiffness measurement values from stage A to stage D ( P < .05). ANOVA analysis showed that the overall liver stiffness measurement among the four BCLC stages was found to be statistically significant different in HBV‐infected and HCV‐infected HCC patients.
Conclusion
Majority (99.24%) were patients aged >40 years old. Male is a high incidence population. In etiological analysis, HBV dominates HCC occurrence, HBV‐, HCV‐, and alcohol‐associated HCC have distinct clinical and biochemical characteristics, necessitating different screening policies to optimize HCC surveillance and management.
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Rising incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found