- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Modulation of anxiety by cortical serotonin 1A receptors
Read this article at
Abstract
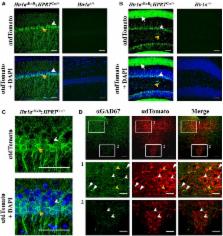
Serotonin (5-HT) plays an important role in the modulation of behavior across animal species. The serotonin 1A receptor (Htr1a) is an inhibitory G-protein coupled receptor that is expressed both on serotonin and non-serotonin neurons in mammals. Mice lacking Htr1a show increased anxiety behavior suggesting that its activation by serotonin has an anxiolytic effect. This outcome can be mediated by either Htr1a population present on serotonin (auto-receptor) or non-serotonin neurons (hetero-receptor), or both. In addition, both transgenic and pharmacological studies have shown that serotonin acts on Htr1a during development to modulate anxiety in adulthood, demonstrating a function for this receptor in the maturation of anxiety circuits in the brain. However, previous studies have been equivocal about which Htr1a population modulates anxiety behavior, with some studies showing a role of Htr1a hetero-receptor and others implicating the auto-receptor. In particular, cell-type specific rescue and suppression of Htr1a expression in either forebrain principal neurons or brainstem serotonin neurons reached opposite conclusions about the role of the two populations in the anxiety phenotype of the knockout. One interpretation of these apparently contradictory findings is that the modulating role of these two populations depends on each other. Here we use a novel Cre-dependent inducible allele of Htr1a in mice to show that expression of Htr1a in cortical principal neurons is sufficient to modulate anxiety. Together with previous findings, these results support a hetero/auto-receptor interaction model for Htr1a function in anxiety.
Related collections
Most cited references61
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Correction of multi-gene deficiency in vivo using a single 'self-cleaving' 2A peptide-based retroviral vector.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Widespread recombinase expression using FLPeR (flipper) mice.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found