- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach in ANCA-Associated Glomerulonephritis: A Review on Management Strategies
Read this article at
Abstract
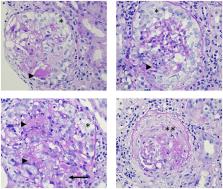
Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis is a destructive small vessel vasculitis affecting multiple organs. Renal involvement often leads to end-stage renal disease and increases mortality. Prompt diagnosis and initiation of adequate immunosuppressive therapy are critical for the best patient and kidney outcomes. However, considerable heterogeneity in symptoms and severity across the patients frequently hinder the diagnosis and management. The objective of this review is to emphasize the heterogeneity of the ANCA-associated vasculitis, facilitate the recognition and give guidance to the therapeutical possibilities. We present epidemiologic and risk factors, pathogenesis, and provide comprehensive clinical features of the disease. This article also focuses on the currently available therapeutic options and emerging cellular and molecular targets for the management of systemic and especially renal disease. We conducted extensive literature research published on PubMed and Google Scholar. We systematically reviewed, analyzed, and assembled databases, covering a broad spectrum of aspects of the disease. We compared and summarized the recommendations of two recent guidelines on ANCA-associated vasculitis. The incidence of ANCA-associated vasculitis, hence glomerulonephritis shows a steady increase. Familiarity with the presenting symptoms and laboratory abnormalities are necessary for rapid diagnosis. Early initiation of treatment is the key aspect for favorable patient and renal outcomes. A better understanding of the pathogenesis constantly leads to more targeted and therefore more efficient and less toxic treatment.
Related collections
Most cited references197
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Neutrophil extracellular traps in immunity and disease
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
KDIGO 2021 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Glomerular Diseases
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found