- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Effects of ginsenoside Re on LPS-induced inflammatory mediators in BV2 microglial cells
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
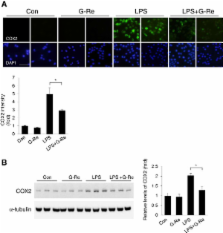
Microglial activation plays an important role in neurodegenerative diseases by producing several pro-inflammatory enzymes and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation leads to the activation of microglial cells in the central nervous system (CNS) and is associated with the pathological mechanisms of neurodegenerative diseases, including PD, AD, and ALS. Ginseng is a natural antioxidant used in herbal medicine and contains ginsenosides (Rb1, Rg1, Rg3, Re, and Rd), which have anti-neoplastic and anti-stress properties.
This study demonstrates the involvement of the anti-inflammatory signaling pathway, ginsenoside-Re (G-Re), which is one of the ginsenosides mediated by LPS-induced neuroinflammation in BV2 microglial cells.
Methods
BV2 microglial cells were pretreated with 2 μg/ml G-Re and stimulated with 1 μg/ml LPS to induce neuroinflammation. To investigate the effect of G-Re on LPS-induced cell signaling, we performed western blotting and immunofluorescence using specific antibodies, such as phospho-p38, COX2, and iNOS.
Related collections
Most cited references28
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Microglia and inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration: multiple triggers with a common mechanism.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Inflammatory neurodegeneration and mechanisms of microglial killing of neurons.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found