- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Tissue Transglutaminase (TG2)-Induced Inflammation in Initiation, Progression, and Pathogenesis of Pancreatic Cancer
Read this article at
Abstract
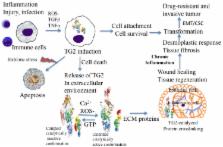
Pancreatic cancer (PC) is among the deadliest cancers, with a median survival of six months. It is generally believed that infiltrating PC arises through the progression of early grade pancreatic intraepithelial lesions (PanINs). In one model of the disease, the K-ras mutation is an early molecular event during progression of pancreatic cancer; it is followed by the accumulation of additional genetic abnormalities. This model has been supported by animal studies in which activated K-ras and p53 mutations produced metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice. According to this model, oncogenic K-ras induces PanIN formation but fails to promote the invasive stage. However, when these mice are subjected to caerulein treatment, which induces a chronic pancreatitis-like state and inflammatory response, PanINs rapidly progress to invasive carcinoma. These results are consistent with epidemiologic studies showing that patients with chronic pancreatitis have a much higher risk of developing PC. In line with these observations, recent studies have revealed elevated expression of the pro-inflammatory protein tissue transglutaminase (TG2) in early PanINs, and its expression increases even more as the disease progresses. In this review we discuss the implications of increased TG2 expression in initiation, progression, and pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer.
Related collections
Most cited references61
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
NF-kappaB in cancer: from innocent bystander to major culprit.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found