- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Australian dingo is an early offshoot of modern breed dogs
Read this article at
Abstract
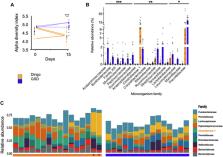
Dogs are uniquely associated with human dispersal and bring transformational insight into the domestication process. Dingoes represent an intriguing case within canine evolution being geographically isolated for thousands of years. Here, we present a high-quality de novo assembly of a pure dingo (CanFam_DDS). We identified large chromosomal differences relative to the current dog reference (CanFam3.1) and confirmed no expanded pancreatic amylase gene as found in breed dogs. Phylogenetic analyses using variant pairwise matrices show that the dingo is distinct from five breed dogs with 100% bootstrap support when using Greenland wolf as the outgroup. Functionally, we observe differences in methylation patterns between the dingo and German shepherd dog genomes and differences in serum biochemistry and microbiome makeup. Our results suggest that distinct demographic and environmental conditions have shaped the dingo genome. In contrast, artificial human selection has likely shaped the genomes of domestic breed dogs after divergence from the dingo.
Abstract
Abstract
A high-quality Australian dingo genome gives a multithousand-year-old snapshot in the evolutionary history of dogs.
Related collections
Most cited references100

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
