- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Sensitive and specific multi-cancer detection and localization using methylation signatures in cell-free DNA
Abstract
Background:
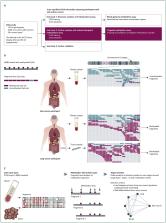
Early cancer detection could identify tumors at a time when outcomes are superior and treatment is less morbid. This prospective case-control sub-study (from NCT02889978 and NCT03085888) assessed the performance of targeted methylation analysis of circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) to detect and localize multiple cancer types across all stages at high specificity.
Participants and methods:
The 6689 participants [2482 cancer (>50 cancer types), 4207 non-cancer] were divided into training and validation sets. Plasma cfDNA underwent bisulfite sequencing targeting a panel of >100 000 informative methylation regions. A classifier was developed and validated for cancer detection and tissue of origin (TOO) localization.
Results:
Performance was consistent in training and validation sets. In validation, specificity was 99.3% [95% confidence interval (CI): 98.3% to 99.8%; 0.7% false-positive rate (FPR)]. Stage I–III sensitivity was 67.3% (CI: 60.7% to 73.3%) in a pre-specified set of 12 cancer types (anus, bladder, colon/rectum, esophagus, head and neck, liver/bile-duct, lung, lymphoma, ovary, pancreas, plasma cell neoplasm, stomach), which account for ~63% of US cancer deaths annually, and was 43.9% (CI: 39.4% to 48.5%) in all cancer types. Detection increased with increasing stage: in the pre-specified cancer types sensitivity was 39% (CI: 27% to 52%) in stage I, 69% (CI: 56% to 80%) in stage II, 83% (CI: 75% to 90%) in stage III, and 92% (CI: 86% to 96%) in stage IV. In all cancer types sensitivity was 18% (CI: 13% to 25%) in stage I, 43% (CI: 35% to 51%) in stage II, 81% (CI: 73% to 87%) in stage III, and 93% (CI: 87% to 96%) in stage IV. TOO was predicted in 96% of samples with cancer-like signal; of those, the TOO localization was accurate in 93%.
Related collections
Most cited references27
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more "personalized" approach to cancer staging.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found