- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Dermatitis Herpetiformis: A Common Extraintestinal Manifestation of Coeliac Disease
Read this article at
Abstract
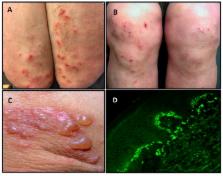
Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) is a common extraintestinal manifestation of coeliac disease presenting with itchy papules and vesicles on the elbows, knees, and buttocks. Overt gastrointestinal symptoms are rare. Diagnosis of DH is easily confirmed by immunofluorescence biopsy showing pathognomonic granular immunoglobulin A (IgA) deposits in the papillary dermis. A valid hypothesis for the immunopathogenesis of DH is that it starts from latent or manifest coeliac disease in the gut and evolves into an immune complex deposition of high avidity IgA epidermal transglutaminase (TG3) antibodies, together with the TG3 enzyme, in the papillary dermis. The mean age at DH diagnosis has increased significantly in recent decades and presently is 40–50 years. The DH to coeliac disease prevalence ratio is 1:8 in Finland and the United Kingdom (U.K.). The annual DH incidence rate, currently 2.7 per 100,000 in Finland and 0.8 per 100,000 in the U.K., is decreasing, whereas the reverse is true for coeliac disease. The long-term prognosis of DH patients on a gluten-free diet is excellent, with the mortality rate being even lower than for the general population.
Related collections
Most cited references50
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Prevalence of celiac disease in at-risk and not-at-risk groups in the United States: a large multicenter study.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Systematic review: worldwide variation in the frequency of coeliac disease and changes over time.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found