scite_
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Speciation and infrageneric classification in the planktonic dinoflagellate Tripos (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae)
Preprint
In review
research-article
31 August 2020
Abstract
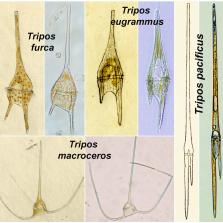
The genus Tripos , formerly marine species of Ceratium , is the dinoflagellate with the greatest number of species and infraspecific taxa (~800) due to the high morphological intraspecific variability of numerous species. In the past, the species of Tripos were proposed into distinct genera. A re-instatement of this generic split is not justified due the difficulties to circumscribe the basal subgenera Amphiceratium and Archaeceratium , and the polyphyletic character of Biceratium . A new infrageneric classification is proposed. The subgenus Amphiceratium is dismembered after the classification of the sections Inflata and partially Fusiformia into Archaeceratium . The subgenus Tripos (autonym) replaces other names such as Tripoceratium or Orthoceratium . Based on the original descriptions, the records of T. furca and T. lineatus correspond to T. eugrammus and T. furca , respectively, and T. macroceros has been reported as T. contrarius . The names T. belone and T. carriensis have been misapplied for T. pacificus and T. volans , respectively. Tripos arcuatus , T. gracilis , T. inclinatus , T. scapiformis and T. subcontortus are revived to replace T. euarcuatus , T. declinatus , T. horridus , T. longirostrum and T. contortus , respectively. The species T. ramakrishnae and T. fusus var. schuettii were described from individuals infected by endoparasites. Tripos rotundatus comb. nov . is proposed for C. digitatum var. rotundatum. As a result of taxonomic revision, Tripos is restricted to 57 correct species, although the speciation and synonymy is largely incomplete due to lack of studies in the life cycle and molecular data.
Content
Author and article information
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).