- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
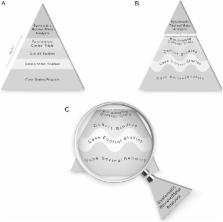
New evidence pyramid
research-article
Read this article at
There is no author summary for this article yet. Authors can add summaries to their articles on ScienceOpen to make them more accessible to a non-specialist audience.
Abstract
A pyramid has expressed the idea of hierarchy of medical evidence for so long, that not all evidence is the same. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses have been placed at the top of this pyramid for several good reasons. However, there are several counterarguments to this placement. We suggest another way of looking at the evidence-based medicine pyramid and explain how systematic reviews and meta-analyses are tools for consuming evidence—that is, appraising, synthesising and applying evidence.
Related collections
Most cited references7
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
How to read a systematic review and meta-analysis and apply the results to patient care: users' guides to the medical literature.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Association between analytic strategy and estimates of treatment outcomes in meta-analyses.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Meta-analysis as evidence: building a better pyramid.
Jesse Berlin, Robert M Golub (2014)