- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRGP): Pleiotropic and paradoxical effects on macrophage, tumor microenvironment, angiogenesis, and other physiological and pathological processes
Abstract
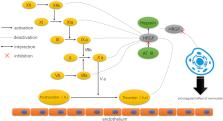
Histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRGP) is a relatively less known glycoprotein, but it is abundant in plasma with a multidomain structure, which allows it to interact with many ligands and regulate various biological processes. HRGP ligands includes heme, Zn 2+, thrombospondin, plasmin/plasminogen, heparin/heparan sulfate, fibrinogen, tropomyosin, IgG, FcγR, C1q. In many conditions, the histidine-rich region of HRGP strengthens ligand binding following interaction with Zn 2+ or exposure to low pH, such as sites of tissue injury or tumor growth. The multidomain structure and diverse ligand binding attributes of HRGP indicates that it can act as an extracellular adaptor protein, connecting with different ligands, especially on cell surfaces. Also, HRGP can selectively target IgG, which blocks the production of soluble immune complexes. The most common cell surface ligand of HRGP is heparan sulfate proteoglycan, and the interaction is also potentiated by elevated Zn 2+ concentration and low pH. Recent reports have shown that HRGP can modulate macrophage polarization and possibly regulate other physiological processes such as angiogenesis, anti-tumor immune response, fibrinolysis and coagulation, soluble immune complex clearance and phagocytosis of apoptotic/necrosis cells. In addition, it has also been reported that HRGP has antibacterial and anti-HIV infection effects and may be used as a novel clinical biomarker accordingly. This review outlines the molecular, structural and biological properties of HRGP as well as presenting an update on the function of HRGP in various physiological processes.
Related collections
Most cited references90
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Macrophage polarization: tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found