- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Molecular pathogenesis of the myeloproliferative neoplasms
Read this article at
Abstract
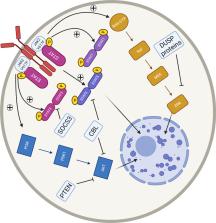
The Philadelphia negative myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) compromise a heterogeneous group of clonal myeloid stem cell disorders comprising polycythaemia vera, essential thrombocythaemia and primary myelofibrosis. Despite distinct clinical entities, these disorders are linked by morphological similarities and propensity to thrombotic complications and leukaemic transformation. Current therapeutic options are limited in disease-modifying activity with a focus on the prevention of thrombus formation. Constitutive activation of the JAK/STAT signalling pathway is a hallmark of pathogenesis across the disease spectrum with driving mutations in JAK2, CALR and MPL identified in the majority of patients. Co-occurring somatic mutations in genes associated with epigenetic regulation, transcriptional control and splicing of RNA are variably but recurrently identified across the MPN disease spectrum, whilst epigenetic contributors to disease are increasingly recognised. The prognostic implications of one MPN diagnosis may significantly limit life expectancy, whilst another may have limited impact depending on the disease phenotype, genotype and other external factors. The genetic and clinical similarities and differences in these disorders have provided a unique opportunity to understand the relative contributions to MPN, myeloid and cancer biology generally from specific genetic and epigenetic changes. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the molecular pathophysiology of MPN exploring the role of driver mutations, co-occurring mutations, dysregulation of intrinsic cell signalling, epigenetic regulation and genetic predisposing factors highlighting important areas for future consideration.
Related collections
Most cited references153
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found