- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Targeting obesity-related dysfunction in hormonally driven cancers
Read this article at
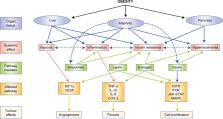
Abstract
Obesity is a risk factor for at least 13 different types of cancer, many of which are hormonally driven, and is associated with increased cancer incidence and morbidity. Adult obesity rates are steadily increasing and a subsequent increase in cancer burden is anticipated. Obesity-related dysfunction can contribute to cancer pathogenesis and treatment resistance through various mechanisms, including those mediated by insulin, leptin, adipokine, and aromatase signalling pathways, particularly in women. Furthermore, adiposity-related changes can influence tumour vascularity and inflammation in the tumour microenvironment, which can support tumour development and growth. Trials investigating non-pharmacological approaches to target the mechanisms driving obesity-mediated cancer pathogenesis are emerging and are necessary to better appreciate the interplay between malignancy, adiposity, diet and exercise. Diet, exercise and bariatric surgery are potential strategies to reverse the cancer-promoting effects of obesity; trials of these interventions should be conducted in a scientifically rigorous manner with dose escalation and appropriate selection of tumour phenotypes and have cancer-related clinical and mechanistic endpoints. We are only beginning to understand the mechanisms by which obesity effects cell signalling and systemic factors that contribute to oncogenesis. As the rates of obesity and cancer increase, we must promote the development of non-pharmacological lifestyle trials for the treatment and prevention of malignancy.
Related collections
Most cited references236
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Gut microbiome modulates response to anti–PD-1 immunotherapy in melanoma patients
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found