- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Using 2-dimensional hand photographs to predict postoperative biochemical remission in acromegaly patients: a transfer learning approach
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
The primary treatment goals in acromegaly patients are complete surgical removal of underlying pituitary tumors and biochemical remission. One of the challenges in developing countries is the difficulty in monitoring postoperative biochemical levels in acromegaly patients, particularly those who live in remote areas or regions with limited medical resources.
Methods
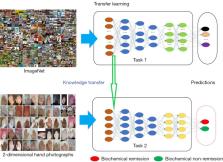
In an attempt to overcome the abovementioned challenges, we conducted a retrospective study and established a mobile and low-cost method to predict biochemical remission in acromegaly patients after surgery, the efficacy of which was assessed retrospectively using the China Acromegaly Patient Association (CAPA) database. A total of 368 surgical patients from the CAPA database were successfully followed up to obtain their hand photographs. Demographics, baseline clinical characteristics, pituitary tumor features, and treatment details were collated. Postoperative outcome, defined as biochemical remission at the last follow-up timepoint, was assessed. Transfer learning with a new mobile tailored neurocomputing architecture, MobileNetv2, was used to explore the identical features that could be used as predictors of long-term biochemical remission after surgery.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms
