- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Comparative study on the performance of solar still equipped with local clay as an energy storage material
Read this article at
Abstract
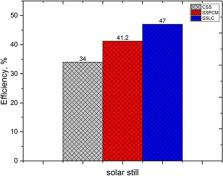
The paucity of freshwater is very dangerous in the coming years. Many coastal countries suffer from a scarcity of freshwater. Solar desalination is the cheapest way to produce freshwater from any type of non-drinkable water (brackish water and seawater). In this work, single-slope single-basin solar still for seawater desalination was examined under Upper Egyptian weather conditions of Qena City (latitude 26.16°, longitude 32.71°). The main goal of the work is to compare the performance of conventional solar still, solar still supported with PCM, and solar still supported with local clay material to augment the solar still yield during both daytime and nighttime periods of operation. The results demonstrated that the total production of desalinated water from the simple conventional solar still, the solar still with PCM, and the solar still with local clay reached about 3885, 4704, and 5388.6 ml/m 2, respectively. Moreover, compared to the conventional solar still, the yield was increased by about 21% when using the PCM, and about 38.7% when using the local clay material. Furthermore, it can be observed that the daytime productivity in the case of solar still supported with local clay was higher than that for the solar still supported with PCM, while the nighttime productivity was higher in the case of solar still supported with PCM compared with solar still supported with local clay. Moreover, the average daily efficiency of conventional solar still, solar still with PCM, and solar still with local clay reached about 34, 41.2, and 47%, respectively. Therefore, it is recommended to use the solar still with local clay for seawater desalination in such arid and hot climate of Qena City.
Related collections
Most cited references48
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Single basin double slope solar still with minimum basin depth and energy storing materials
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Thermal performance of a single basin solar still with PCM as a storage medium
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found