- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Establishing a population-based patient-reported outcomes study (PROMs) using national cancer registries across two jurisdictions: the Prostate Cancer Treatment, your experience (PiCT ure) study
Read this article at
Abstract
Objective
To establish an international patient-reported outcomes (PROMs) study among prostate cancer survivors, up to 18 years postdiagnosis, in two countries with different healthcare systems and ethical frameworks.
Design
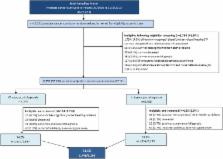
A cross-sectional, postal survey of prostate cancer survivors sampled and recruited via two population-based cancer registries. Healthcare professionals (HCPs) evaluated patients for eligibility to participate. Questionnaires contained validated instruments to assess health-related quality of life and psychological well-being, including QLQ-C30, QLQ-PR25, EQ-5D-5L, 21-question Depression, Anxiety and Stress Scale (DASS-21) and the Decisional Regret Scale.
Primary outcome measures
Registration completeness, predictors of eligibility and response, data missingness, unweighted and weighted PROMs.
Results
Prostate cancer registration was 80% (95% CI 75% to 84%) and 91% (95% CI 89% to 93%) complete 2 years postdiagnosis in NI and RoI, respectively. Of 12 322 survivors sampled from registries, 53% (n=6559) were classified as eligible following HCP screening. In the multivariate analysis, significant predictors of eligibility were: being ≤59 years of age at diagnosis (p<0.001), short-term survivor (<5 years postdiagnosis; p<0.001) and from RoI (p<0.001). 3348 completed the questionnaire, yielding a 54% adjusted response rate. 13% of men or their families called the study freephone with queries for assistance with questionnaire completion or to talk about their experience. Significant predictors of response in multivariate analysis were: being ≤59 years at diagnosis (p<0.001) and from RoI (p=0.016). Mean number of missing questions in validated instruments ranged from 0.12 (SD 0.71; EQ-5D-5L) to 3.72 (SD 6.30; QLQ-PR25). Weighted and unweighted mean EQ-5D-5L, QLQ-C30 and QLQ-PR25 scores were similar, as were the weighted and unweighted prevalences of depression, anxiety and distress.
Conclusions
It was feasible to perform PROMs studies across jurisdictions, using cancer registries as sampling frames; we amassed one of the largest, international, population-based data set of prostate cancer survivors. We highlight improvements which could inform future PROMs studies, including utilising general practitioners to assess eligibility and providing a freephone service.
Related collections
Most cited references16
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Practical and statistical issues in missing data for longitudinal patient-reported outcomes.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found