- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A functional near-infrared spectroscopy study on hemodynamic changes of patients with prolonged disorders of consciousness responding to different auditory stimuli
Read this article at
Abstract
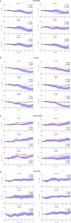
Treating prolonged disorders of consciousness (pDoC) is challenging. Thus, accurate assessment of residual consciousness in patients with pDoC is important for the management and recovery of patients. Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) can be used to detect brain activity through changes of oxygenated hemoglobin/deoxygenated hemoglobin (HbO/HbR) concentrations changes and has recently gained increasing attention for its potential applications in assessing residual consciousness. However, the number of fNIRS studies assessing residual awareness in patients with pDoC is still limited. In this study, fNIRS was used to evaluate the brain function in 18 patients with pDoC, including 14 vegetative states (VS) and 4 minimally conscious states (MCS), and 15 healthy controls (HC). All participants accepted two types of external stimuli, i.e., active stimulation (motor imagery, MI) and passive stimulation (subject’s own name, SON). The results showed that the mean concentrations of HbO/HbR in the prefrontal cortex of the HC during the passive stimulation were significantly lower than those of the active stimulation, and the fitting slope was high. However, the hemodynamic responses of the patients with pDoC were opposite to those of the HC. Additionally, the mean concentrations of HbO/HbR increased as the level of consciousness decreased during passive stimulation. Our findings suggest that the residual level of consciousness in pDoC patients can be assessed by measuring brain responses to different stimulations using fNIRS. The present study further demonstrates the feasibility and reliability of fNIRS in assessing residual consciousness in patients with pDoC, providing a basis for its expanded clinical application.
Related collections
Most cited references36
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The JFK Coma Recovery Scale-Revised: measurement characteristics and diagnostic utility.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Experimental and theoretical approaches to conscious processing.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Functional near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) signal improvement based on negative correlation between oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin dynamics.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.