- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Microbial Profile of Fresh and Semicooked Nile Tilapia ( Oreochromis niloticus) and Hygienic Practice of Fish Handlers in Hawassa, Ethiopia
Read this article at
Abstract
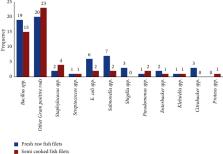
Despite its high nutritional quality, fish is a highly perishable food item. This study aimed at assessing the microbial quality and safety of fresh and semicooked Nile tilapia fish fillets and the food safety practices of fish handlers in Hawassa City. The microbial load of 40 for each of raw and semicooked fillet samples was estimated by the standard plate count method, and the dominant flora as well as common bacterial pathogens were identified following phenotypic procedures. Moreover, a survey was conducted to assess the hygienic conditions and food safety practices of 30 fish handlers. The mean microbial load of the raw fillet samples in log 10CFUg −1 was 8.42 for aerobic mesophilic bacteria (AMBC), 2.52 for total coliforms (TCC), and 3.41 for a count of staphylococci (CS). On the other hand, the respective parameters for the semicooked fillets in log 10CFUg −1 were 6.68 (AMBC), 2.52 (TCC), and 3.17 (CS). The mean AMBC of all the fresh raw fillet samples exceeded the recommended maximum permissible limits. The mean SC of raw fillets from three of the eight vendors and one semicooked fillet were at a potentially hazardous level (>4 log units). Moreover, Salmonella species were isolated from 30% to 25% of raw and semicooked samples, respectively. The mesophilic bacterial flora of both types of samples was dominated by Bacillus species, Salmonella species, E coli, and Staphylococcus species. Most fish handlers did not practice hygienic food handling and lacked basic sanitation amenities like clean water and soap for hand washing. Moreover, nearly all the fish handlers did not have any formal education. These findings call for public health intervention measures like the provision of training in good hygienic practices and certification for fish vendors in the chain.
Related collections
Most cited references70
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Recent advances in understanding enteric pathogenic Escherichia coli.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Staphylococcus aureus and its food poisoning toxins: characterization and outbreak investigation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found