- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Ameliorative Effects of Peptides from the Oyster ( Crassostrea hongkongensis) Protein Hydrolysates against UVB-Induced Skin Photodamage in Mice
Read this article at
Abstract
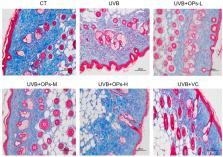
Chronic exposure to ultraviolet B (UVB) irradiation is a major cause for skin photoaging. UVB induces damage to skin mainly by oxidative stress, inflammation, and collagen degradation. This paper investigated the photo-protective effects of peptides from oyster ( Crassostrea hongkongensis) protein hydrolysates (OPs) by topical application on the skin of UVB-irradiated mice. Results from mass spectrometry showed that OPs consisted of peptides with a molecular weight range of 302.17–2936.43 Da. In vivo study demonstrated that topical application of OPs on the skin significantly alleviated moisture loss, epidermal hyperplasia, as well as degradation of collagen and elastin fibers caused by chronic UVB irradiation. In this study, OPs treatment promoted antioxidant enzymes (SOD and GPH-Px) activities, while decreased malondialdehyde (MDA) level in the skin. In addition, OPs treatment significantly decreased inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α) content, and inhibited inflammation related (iNOS, COX-2) protein expression in the skin. Via inhibiting metalloproteinase 1(MMP1) expression, OPs treatment markedly decreased the degradation of collagen and elastin fibers as well as recovered the altered arrangement of extracellular matrix network in the dermis of skin. Our study demonstrated for the first time that OPs protected against UVB induced skin photodamage by virtue of its antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as regulating the abnormal expression of MMP-1. The possible molecular mechanism underlying OPs anti-photoaging is possibly related to downregulating of the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway, while promoting TGF-β production in the skin.
Related collections
Most cited references40
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Pathophysiology of premature skin aging induced by ultraviolet light.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
UV-light-induced signal cascades and skin aging.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Immunomodulatory and anticancer protein hydrolysates (peptides) from food proteins: A review.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.