- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Inorganic Chemical Fertilizer Application to Wheat Reduces the Abundance of Putative Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria
Read this article at
Abstract
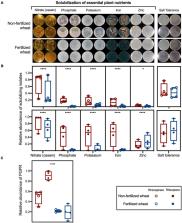
The profound negative effect of inorganic chemical fertilizer application on rhizobacterial diversity has been well documented using 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing and predictive metagenomics. We aimed to measure the function and relative abundance of readily culturable putative plant growth-promoting rhizobacterial (PGPR) isolates from wheat root soil samples under contrasting inorganic fertilization regimes. We hypothesized that putative PGPR abundance will be reduced in fertilized relative to unfertilized samples. Triticum aestivum cv. Cadenza seeds were sown in a nutrient depleted agricultural soil in pots treated with and without Osmocote ® fertilizer containing nitrogen-phosphorous-potassium (NPK). Rhizosphere and rhizoplane samples were collected at flowering stage (10 weeks) and analyzed by culture-independent (CI) amplicon sequence variant (ASV) analysis of rhizobacterial DNA as well as culture-dependent (CD) techniques. Rhizosphere and rhizoplane derived microbiota culture collections were tested for plant growth-promoting traits using functional bioassays. In general, fertilizer addition decreased the proportion of nutrient-solubilizing bacteria (nitrate, phosphate, potassium, iron, and zinc) isolated from rhizocompartments in wheat whereas salt tolerant bacteria were not affected. A “PGPR” database was created from isolate 16S rRNA gene sequences against which total amplified 16S rRNA soil DNA was searched, identifying 1.52% of total community ASVs as culturable PGPR isolates. Bioassays identified a higher proportion of PGPR in non-fertilized samples [rhizosphere (49%) and rhizoplane (91%)] compared to fertilized samples [rhizosphere (21%) and rhizoplane (19%)] which constituted approximately 1.95 and 1.25% in non-fertilized and fertilized total community DNA, respectively. The analyses of 16S rRNA genes and deduced functional profiles provide an in-depth understanding of the responses of bacterial communities to fertilizer; our study suggests that rhizobacteria that potentially benefit plants by mobilizing insoluble nutrients in soil are reduced by chemical fertilizer addition. This knowledge will benefit the development of more targeted biofertilization strategies.
Related collections
Most cited references76

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
DADA2: High resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found