- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Selective Small Molecule Induced Degradation of the BET Bromodomain Protein BRD4
Read this article at
Abstract

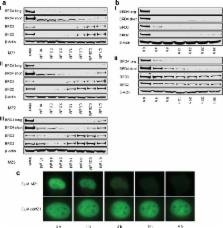
The Bromo- and Extra-Terminal (BET) proteins BRD2, BRD3, and BRD4 play important roles in transcriptional regulation, epigenetics, and cancer and are the targets of pan-BET selective bromodomain inhibitor JQ1. However, the lack of intra-BET selectivity limits the scope of current inhibitors as probes for target validation and could lead to unwanted side effects or toxicity in a therapeutic setting. We designed Proteolysis Targeted Chimeras (PROTACs) that tether JQ1 to a ligand for the E3 ubiquitin ligase VHL, aimed at triggering the intracellular destruction of BET proteins. Compound MZ1 potently and rapidly induces reversible, long-lasting, and unexpectedly selective removal of BRD4 over BRD2 and BRD3. The activity of MZ1 is dependent on binding to VHL but is achieved at a sufficiently low concentration not to induce stabilization of HIF-1α. Gene expression profiles of selected cancer-related genes responsive to JQ1 reveal distinct and more limited transcriptional responses induced by MZ1, consistent with selective suppression of BRD4. Our discovery opens up new opportunities to elucidate the cellular phenotypes and therapeutic implications associated with selective targeting of BRD4.
Related collections
Most cited references23
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Protacs: chimeric molecules that target proteins to the Skp1-Cullin-F box complex for ubiquitination and degradation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Structural basis for the recognition of hydroxyproline in HIF-1 alpha by pVHL.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
