- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A novel transgenic mouse model of CBS-deficient homocystinuria does not incur hepatic steatosis or fibrosis and exhibits a hypercoagulative phenotype that is ameliorated by betaine treatment
Read this article at
Abstract
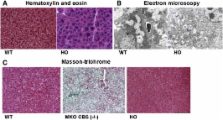
Cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) catalyzes the condensation of homocysteine (Hcy) and serine to cystathionine, which is then hydrolyzed to cysteine by cystathionine gamma-lyase. Inactivation of CBS results in CBS-deficient homocystinuria more commonly referred to as classical homocystinuria, which, if untreated, results in mental retardation, thromboembolic complications, and a range of connective tissue disorders. The molecular mechanisms that underlie the pathology of this disease are poorly understood. We report here the generation of a new mouse model of classical homocystinuria in which the mouse cbs gene is inactivated and that exhibits low-level expression of the human CBS transgene under the control of the human CBS promoter. This mouse model, designated “human only” (HO), exhibits severe elevations in both plasma and tissue levels of Hcy, methionine, S-adenosylmethionine, and S-adenosylhomocysteine and a concomitant decrease in plasma and hepatic levels of cysteine. HO mice exhibit mild hepatopathy but, in contrast to previous models of classical homocystinuria, do not incur hepatic steatosis, fibrosis, or neonatal death with approximately 90% of HO mice living for at least 6 months. Tail bleeding determinations indicate that HO mice are in a hypercoagulative state that is significantly ameliorated by betaine treatment in a manner that recapitulates the disease as it occurs in humans. Our findings indicate that this mouse model will be a valuable tool in the study of pathogenesis in classical homocystinuria and the rational design of novel treatments.
Related collections
Most cited references25
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Relative contributions of cystathionine beta-synthase and gamma-cystathionase to H2S biogenesis via alternative trans-sulfuration reactions.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mice deficient in cystathionine beta-synthase: animal models for mild and severe homocyst(e)inemia.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
