- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Clinical Potential and Current Progress of Dental Pulp Stem Cells for Various Systemic Diseases in Regenerative Medicine: A Concise Review
Read this article at
Abstract
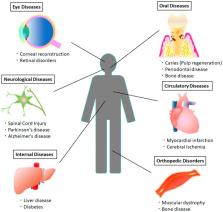
Dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) are mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) that have multipotent differentiation and a self-renewal ability. They have been useful not only for dental diseases, but also for systemic diseases. Extensive studies have suggested that DPSCs are effective for various diseases, such as spinal cord injuries, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, cerebral ischemia, myocardial infarction, muscular dystrophy, diabetes, liver diseases, eye diseases, immune diseases, and oral diseases. DPSCs have the potential for use in a cell-therapeutic paradigm shift to treat these diseases. It has also been reported that DPSCs have higher regenerative potential than the bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells known as representative MSCs. Therefore, DPSCs have recently gathered much attention. In this review, the therapeutic potential of DPSCs, the latest progress in the pre-clinical study for treatment of these various systemic diseases, and the clinical applications of DPSCs in regenerative medicine, are all summarized. Although challenges, including mechanisms of the effects and establishment of cell processing and transplantation methods for clinical use, still remain, DPSCs could be promising stem cells sources for various clinical applications, because of their easy isolation by a noninvasive procedure without ethical concerns.
Related collections
Most cited references75
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Characterization of the apical papilla and its residing stem cells from human immature permanent teeth: a pilot study.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Fate of the mammalian cranial neural crest during tooth and mandibular morphogenesis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found