- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Alantolactone: A Natural Plant Extract as a Potential Therapeutic Agent for Cancer
Read this article at
Abstract
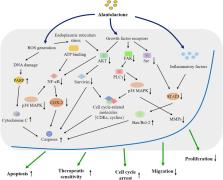
Alantolactone (ALT) is a natural compound extracted from Chinese traditional medicine Inula helenium L. with therapeutic potential in the treatment of various diseases. Recently, in vitro and in vivo studies have indicated cytotoxic effects of ALT on various cancers, including liver cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, etc. The inhibitory effects of ALT depend on several cancer-associated signaling pathways and abnormal regulatory factors in cancer cells. Moreover, emerging studies have reported several promising strategies to enhance the oral bioavailability of ALT, such as combining ALT with other herbs and using ALT-entrapped nanostructured carriers. In this review, studies on the anti-tumor roles of ALT are mainly summarized, and the underlying molecular mechanisms of ALT exerting anticancer effects on cells investigated in animal-based studies are also discussed.
Related collections
Most cited references103
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
NF-κB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: coming of age
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
VEGF in Signaling and Disease: Beyond Discovery and Development
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found