- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Sensitive and Quantitative Detection of MHC-I Displayed Neoepitopes Using a Semiautomated Workflow and TOMAHAQ Mass Spectrometry

Read this article at
Abstract
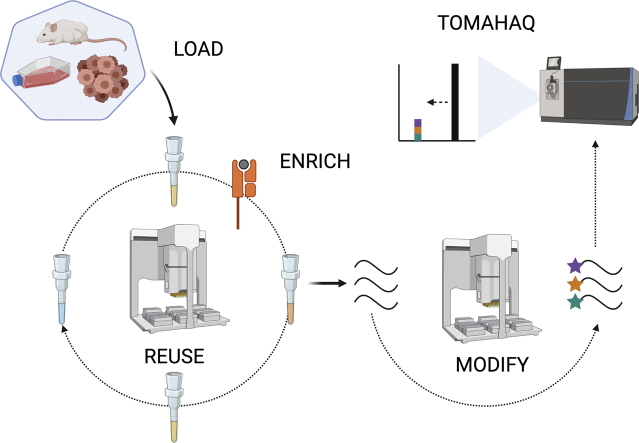
Advances in several key technologies, including MHC peptidomics, have helped fuel our understanding of basic immune regulatory mechanisms and the identification of T cell receptor targets for the development of immunotherapeutics. Isolating and accurately quantifying MHC-bound peptides from cells and tissues enables characterization of dynamic changes in the ligandome due to cellular perturbations. However, the current multistep analytical process is challenging, and improvements in throughput and reproducibility would enable rapid characterization of multiple conditions in parallel. Here, we describe a robust and quantitative method whereby peptides derived from MHC-I complexes from a variety of cell lines, including challenging adherent lines such as MC38, can be enriched in a semiautomated fashion on reusable, dry-storage, customized antibody cartridges. Using this method, a researcher, with very little hands-on time and in a single day, can perform up to 96 simultaneous enrichments at a similar level of quality as a manual workflow. TOMAHAQ (Triggered by Offset, Multiplexed, Accurate-mass, High-resolution, and Absolute Quantification), a targeted mass spectrometry technique that combines sample multiplexing and high sensitivity, was employed to characterize neoepitopes displayed on MHC-I by tumor cells and to quantitatively assess the influence of neoantigen expression and induced degradation on neoepitope presentation. This unique combination of robust semiautomated MHC-I peptide isolation and high-throughput multiplexed targeted quantitation allows for both the routine analysis of >4000 unique MHC-I peptides from 250 million cells using nontargeted methods, as well as quantitative sensitivity down to the low amol/μl level using TOMAHAQ targeted MS.
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
Semiautomated peptide immunoprecipitation on reusable antibody cartridges.
-
•
Application of TOMAHAQ for MHC-I detection and quantitation.
-
•
Routine analysis of >4000 unique MHC-I peptides from 250 million cells via automation.
-
•
Quantitative sensitivity down to the low amol/μl level using TOMAHAQ targeted MS.
In Brief
This manuscript highlights a new semiautomated MHC-I peptide immunoprecipitation method used in conjunction with the multiplexed quantitative technique TOMAHAQ (Triggered by Offset, Multiplexed, Accurate-mass, High-resolution, and Absolute Quantification) for the detection and quantitation of MHC-I peptides. This combination of techniques allows the routine analysis of >4000 unique MHC-I peptides from 250 million cells and in with targeted analysis, quantitative sensitivity down to the low amol/μl level.
Related collections
Most cited references51

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Welcome to the Tidyverse

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found