- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Transimmunization restores immune surveillance and prevents recurrence in a syngeneic mouse model of ovarian cancer
Read this article at
ABSTRACT
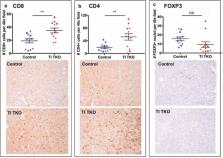
Ovarian cancer accounts for most deaths from gynecologic malignancies. Although more than 80% of patients respond to first-line standard of care, most of these responders present with recurrence and eventually succumb to carcinomatosis and chemotherapy-resistant disease. To improve patient survival, new modalities must, therefore, target or prevent recurrent disease. Here we describe for the first time a novel syngeneic mouse model of recurrent high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC), which allows immunotherapeutic interventions in a time course relevant to human carcinomatosis and disease course. Using this model, we demonstrate the efficacy of Transimmunization (TI), a dendritic cell (DC) vaccination strategy that uses autologous and physiologically derived DC loaded with autologous whole tumor antigens. TI has been proven successful in the treatment of human cutaneous T cell lymphoma and we report for the first time its in vivo efficacy against an intra-peritoneal solid tumor. Given as a single therapy, TI is able to elicit an effective anti-tumor immune response and inhibit immune-suppressive crosstalks with sufficient power to curtail tumor progression and establishment of carcinomatosis and recurrent disease. Specifically, TI is able to inhibit the expansion of tumor-associated macrophages as well as myeloid-derived suppressive cells consequently restoring T cell immune-surveillance. These results demonstrate the possible value of TI in the management of ovarian cancer and other intra-peritoneal tumors.
Related collections
Most cited references52
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating T cells in ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found