- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Hepatitis C-related cryoglobulinemic neuropathy: potential role of oxcarbazepine for pain control
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
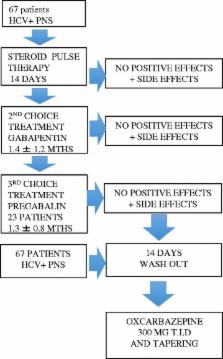
Peripheral neuropathy is one most common, limiting and invalidating neurological symptom in subjects with hepatitis C virus and mixed cryoglobulinemia. Notably, the medical therapy proposed to eradicate HCV, can frequently exacerbate the painful neuropathy. Therefore, neuropathy therapies are insufficient and inadequate, and comprise immunosuppressive drugs, such as steroid or cyclosporine, intravenous immunoglobulin or plasma exchange. These have shown variable success in case reports, with a presumably temporary effect, but with major side effects.
Methods
We assessed the effects of oxcarbazepine treatment in 67 cases of cryoglobulinemia related neuropathy, who did not respond to either steroid or Gabapentin, or Pregabalin. Oxcarbazepine was chosen based on the promising preliminary results.
Related collections
Most cited references45
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The short-form McGill Pain Questionnaire.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Formulation and application of a numerical scoring system for assessing histological activity in asymptomatic chronic active hepatitis
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found