- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A Review of Diabetes Mellitus and Exposure to the Environmental Toxicant Cadmium with an Emphasis on Likely Mechanisms of Action
Read this article at
Abstract
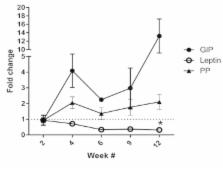
There is increasing interest in how exposure to environmental substances can contribute to the onset of Type II diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Impaired insulin release is a hallmark of type I diabetes mellitus and is involved in the progression of T2DM. Both epidemiological and experimental studies show that exposure to the environmental pollutant cadmium (Cd), is associated with hyperglycemia, T2DM and reduced serum insulin. The goal of this review is to examine likely mechanisms of action of Cd-induced dysglycemia based on experimental studies in the literature and from the most recent findings in the Edwards lab. The primary focus of this review will examine how Cd may cause islet dysfunction and subsequent impaired insulin release. Recent findings in the Edwards lab indicate that Cd causes time-dependent and statistically significant changes in fasting leptin, Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP) and pancreas polypeptide hormone levels in a subchronic animal model of Cd-induced hyperglycemia. This review summarizes the most likely cellular mechanisms by which the ubiquitous environmental contaminant Cd disrupts glucose homeostasis. While individual cellular effects of Cd are reviewed it is likely that no one single mechanism is involved, rather multiple mechanisms exist and work synergistically resulting in islet dysfunction and ultimately dysglycemia.
Related collections
Most cited references56
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Convergence of Wnt, beta-catenin, and cadherin pathways.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
beta-cell failure in diabetes and preservation by clinical treatment.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found