- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Safety and efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy vs. flexible ureteroscopy in the treatment of urinary calculi: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Read this article at
Abstract
Objective
This study aims to compare the safety and efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (SWL) and flexible ureteroscopy lithotripsy (f-URS) in treating urinary tract stones.
Methods
We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane for literature comparing SWL with f-URS. The primary outcomes we focused on were stone-free rate (SFR) and complications; the secondary outcomes were operation time, hospital stay, retreatment rate, number of sessions, and auxiliary procedures rate. We used ReviewManager version 5.4.1 and STATA version 14.2 for meta-analysis.
Results
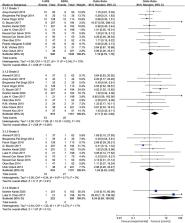
Seventeen studies with a total of 2,265 patients were included in the meta-analysis, including 1,038 patients in the SWL group and 1,227 patients in the f-URS group. The meta-analysis indicated that patients in the f-URS group had higher SFR than those in the SWL group [odds ratio (OR): 2.00, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.29–3.12, p = 0.002]. In addition, we found no significant difference in complications (OR: 1.08, 95% CI: 0.85–1.37) between the two treatments. Also, we found that the retreatment rate and the auxiliary procedure rate in the f-URS group were significantly lower than those in the SWL group (OR: 0.08, 95% CI: 0.02–0.24, p < 0.00001; OR: 0.30, 95% CI: 0.11–0.83, p = 0.02). Moreover, the number of sessions in the f-URS group was significantly lower than that in the SWL group [mean difference (MD): −1.96, 95% CI: −1.55 to −0.33, p = 0.003]. However, the operation time and hospital stay in the f-URS group were significantly longer than those in the SWL group (MD: 11.24, 95% CI: 3.51–18.56, p = 0.004; MD: 1.14, 95% CI: 0.85–1.42, p < 0.00001).
Conclusion
For 1–2-cm urinary stones, f-URS can achieve a higher SFR than SWL while having a lower retreatment rate, number of sessions, and auxiliary procedure rate. For urinary stones <1 cm, there was no significant difference in SFR between SWL and f-URS groups. The SWL group has a shorter operative time and hospital stay than the f-URS group.
Related collections
Most cited references40
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found