- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Development of a Whole-Body Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Approach to Assess the Pharmacokinetics of Drugs in Elderly Individuals
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Because of the vulnerability and frailty of elderly adults, clinical drug development has traditionally been biased towards young and middle-aged adults. Recent efforts have begun to incorporate data from paediatric investigations. Nevertheless, the elderly often remain underrepresented in clinical trials, even though persons aged 65 years and older receive the majority of drug prescriptions. Consequently, a knowledge gap exists with regard to pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) responses in elderly subjects, leaving the safety and efficacy of medicines for this population unclear.
Objectives
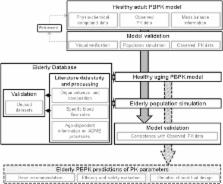
The goal of this study was to extend a physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model for adults to encompass the full course of healthy aging through to the age of 100 years, to support dose selection and improve pharmacotherapy for the elderly age group.
Methods
For parameterization of the PBPK model for healthy aging individuals, the literature was scanned for anthropometric and physiological data, which were consolidated and incorporated into the PBPK software PK-Sim ®. Age-related changes that occur from 65 to 100 years of age were the main focus of this work. For a sound and continuous description of an aging human, data on anatomical and physiological changes ranging from early adulthood to old age were included. The capability of the PBPK approach to predict distribution and elimination of drugs was verified using the test compounds morphine and furosemide, administered intravenously. Both are cleared by a single elimination pathway. PK parameters for the two compounds in younger adults and elderly individuals were obtained from the literature. Matching virtual populations—with regard to age, sex, anthropometric measures and dosage—were generated. Profiles of plasma drug concentrations over time, volume of distribution at steady state ( V ss) values and elimination half-life ( t ½) values from the literature were compared with those predicted by PBPK simulations for both younger adults and the elderly.
Results
For most organs, the age-dependent information gathered in the extensive literature analysis was dense. In contrast, with respect to blood flow, the literature study produced only sparse data for several tissues, and in these cases, linear regression was required to capture the entire elderly age range. On the basis of age-informed physiology, the predicted PK profiles described age-associated trends well. The root mean squared prediction error for the prediction of plasma concentrations of furosemide and morphine in the elderly were improved by 32 and 49 %, respectively, by use of age-informed physiology. The majority of the individual V ss and t ½ values for the two model compounds, furosemide and morphine, were well predicted in the elderly population, except for long furosemide half-lifes.
Conclusion
The results of this study support the feasibility of using a knowledge-driven PBPK aging model that includes the elderly to predict PK alterations throughout the entire course of aging, and thus to optimize drug therapy in elderly individuals. These results indicate that pharmacotherapy and safety-related control of geriatric drug therapy regimens may be greatly facilitated by the information gained from PBPK predictions.
Related collections
Most cited references118
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Epidemiology of sarcopenia among the elderly in New Mexico.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Low relative skeletal muscle mass (sarcopenia) in older persons is associated with functional impairment and physical disability.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found