- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Accuracy of B-mode ultrasound and ARFI elastography in predicting malignancy of canine splenic lesions
Read this article at
Abstract
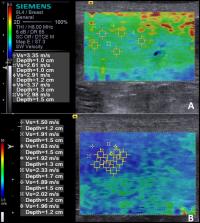
The objective was to evaluate the accuracy of B-mode ultrasonography and ARFI elastography in detecting malignancy in canine splenic lesions. Thirty-seven spleens with abnormalities (16 benign and 21 malignant) from dogs of different breeds and ages were evaluated. Echogenicity, echotexture, organ length and height were evaluated using B-mode. By ARFI elastography, tissue stiffness was evaluated qualitatively (elastogram) and quantitatively (measuring the shear wave velocity—SWV). Lesions were classified as diffuse, focal or multifocal (cranial, medial or caudal portion) and comparisons of the SWV between the injured and non-injured areas were performed. In the B-mode, no features were associated to malignancy (P > 0.05). In the elastogram, 35 spleens were non-deformable and 2 deformable, having no association with malignancy. The greater SWV was observed in malignant lesions (3.4 ± 0.6 m/s), followed by areas free from alterations (2.1 ± 0.3 m/s) and benign lesions (1.7 ± 0.5 m/s), with difference between groups (P < 0.0001). It was found that a SWV > 2.6 m/s indicates malignancy of canine splenic lesions (sensitivity of 95%, specificity of 100%, PPV of 100%, NPV of 94% and accuracy of 97%), concluding that ARFI elastography is a promising technique for differentiating malignancy in these lesions.
Related collections
Most cited references39
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Update to the Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound Liver Elastography Consensus Statement
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Shear wave elastography of thyroid nodules for the prediction of malignancy in a large scale study.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found