- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Attenuated Increase in Maximal Force of Rat Medial Gastrocnemius Muscle after Concurrent Peak Power and Endurance Training
Read this article at
Abstract
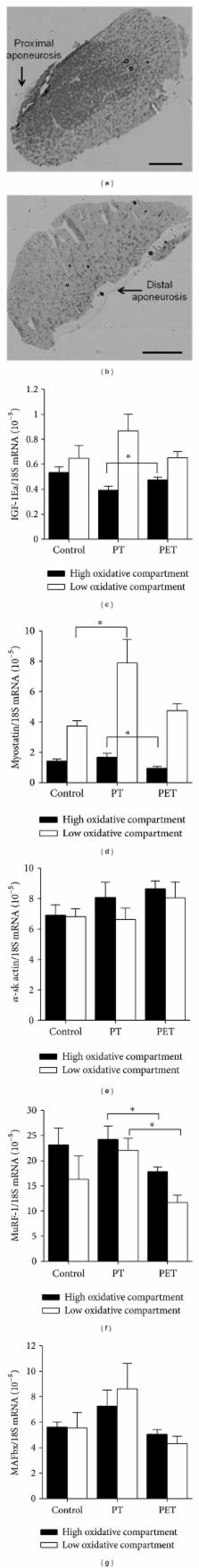
Improvement of muscle peak power and oxidative capacity are generally presumed to be mutually exclusive. However, this may not be valid by using fibre type-specific recruitment. Since rat medial gastrocnemius muscle (GM) is composed of high and low oxidative compartments which are recruited task specifically, we hypothesised that the adaptive responses to peak power training were unaffected by additional endurance training. Thirty rats were subjected to either no training (control), peak power training (PT), or both peak power and endurance training (PET), which was performed on a treadmill 5 days per week for 6 weeks. Maximal running velocity increased 13.5% throughout the training and was similar in both training groups. Only after PT, GM maximal force was 10% higher than that of the control group. In the low oxidative compartment, mRNA levels of myostatin and MuRF-1 were higher after PT as compared to those of control and PET groups, respectively. Phospho-S6 ribosomal protein levels remained unchanged, suggesting that the elevated myostatin levels after PT did not inhibit mTOR signalling. In conclusion, even by using task-specific recruitment of the compartmentalized rat GM, additional endurance training interfered with the adaptive response of peak power training and attenuated the increase in maximal force after power training.
Related collections
Most cited references38
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy signaling pathways.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Myostatin reduces Akt/TORC1/p70S6K signaling, inhibiting myoblast differentiation and myotube size.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found