- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Prognostic Impact of An Integrative Landscape of Clinical, Immune, and Molecular Features in Non-Metastatic Rectal Cancer
Read this article at
Abstract
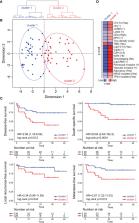
Rectal Cancer (RC) is a complex disease that involves highly variable treatment responses. Currently, there is a lack of reliable markers beyond TNM to deliver a personalized treatment in a cancer setting where the goal is a curative treatment. Here, we performed an integrated characterization of the predictive and prognostic role of clinical features, mismatch-repair deficiency markers, HER2, CDX2, PD-L1 expression, and CD3 −CD8 + tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) coupled with targeted DNA sequencing of 76 non-metastatic RC patients assigned to total mesorectal excision upfront (TME; n = 15) or neoadjuvant chemo-radiotherapy treatment (nCRT; n = 61) followed by TME. Eighty-two percent of RC cases displayed mutations affecting cancer driver genes such as TP53, APC, KRAS, ATM, and PIK3CA. Good response to nCRT treatment was observed in approximately 40% of the RC cases, and poor pathological tumor regression was significantly associated with worse disease-free survival (DFS, HR = 3.45; 95%CI = 1.14–10.4; p = 0.028). High neutrophils-platelets score (NPS) (OR = 10.52; 95%CI=1.34–82.6; p = 0.025) and KRAS mutated cases (OR = 5.49; 95%CI = 1.06–28.4; p = 0.042) were identified as independent predictive factors of poor response to nCRT treatment in a multivariate analysis. Furthermore, a Cox proportional-hazard model showed that the KRAS mutational status was an independent prognostic factor associated with higher risk of local recurrence (HR = 9.68; 95%CI = 1.01–93.2; p <0.05) and shorter DFS (HR = 2.55; 95%CI = 1.05–6.21; p <0.05), while high CEA serum levels were associated with poor DFS (HR = 2.63; 95%CI = 1.01–6.85; p <0.05). Integrated clinical and molecular-based unsupervised analysis allowed us to identify two RC prognostic groups (cluster 1 and cluster 2) associated with disease-specific OS (HR = 20.64; 95%CI = 2.63–162.2; p <0.0001), metastasis-free survival (HR = 3.67; 95%CI = 1.22–11; p = 0.012), local recurrence-free survival (HR = 3.34; 95%CI = 0.96–11.6; p = 0.043) and worse DFS (HR = 2.68; 95%CI = 1.18–6.06; p = 0.012). The worst prognosis cluster 2 was enriched by stage III high-risk clinical tumors, poor responders to nCRT, with low TILs density and high frequency of KRAS and TP53 mutated cases compared with the best prognosis cluster 1 (p <0.05). Overall, this study provides a comprehensive and integrated characterization of non-metastatic RC cases as a new insight to deliver a personalized therapeutic approach.
Related collections
Most cited references74
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
PD-1 Blockade in Tumors with Mismatch-Repair Deficiency.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found